
Brand building is the process of creating and strengthening a brand’s identity, reputation, and presence in the market. It involves various strategies and activities aimed at establishing a unique brand image and connecting with the target audience. The key components of brand building include:
- Brand Identity: This includes the visual elements of a brand, such as the logo, color scheme, typography, and design style. It also encompasses the brand’s voice, tone, and messaging that reflect its personality and values.
- Brand Positioning: Defining the unique value proposition and differentiating the brand from competitors. This involves identifying the target market and crafting a compelling brand promise that resonates with them.
- Brand Awareness: Increasing the visibility and recognition of the brand through various marketing and advertising efforts. This can involve digital marketing, social media, content marketing, public relations, and more.
- Brand Loyalty: Building a strong emotional connection with customers to foster loyalty and repeat business. This can be achieved through exceptional customer service, consistent quality, and engaging experiences.
- Brand Equity: The value that a brand adds to a product or service. Strong brand equity results in higher customer trust, willingness to pay a premium, and overall positive perception of the brand.
- Brand Consistency: Ensuring that all brand communications and interactions are consistent across all channels and touchpoints. Consistency helps reinforce the brand identity and build trust with the audience.
- Customer Engagement: Creating meaningful interactions with customers to build relationships and encourage brand advocacy. This can be done through social media engagement, loyalty programs, personalized experiences, and community building.
Effective brand building requires a strategic approach, creativity, and a deep understanding of the target audience. It is an ongoing process that evolves with the market and consumer preferences.
Brand Building | What it Takes ?

Building a strong brand requires a strategic and multi-faceted approach. Here are the key elements involved in brand building:
1. Understanding Your Audience
- Market Research: Conduct thorough research to understand your target audience’s needs, preferences, and behaviors.
- Customer Personas: Create detailed personas representing different segments of your audience to tailor your brand messaging.
2. Defining Your Brand Identity
- Brand Purpose: Clearly articulate the mission and vision of your brand.
- Brand Values: Identify the core values that guide your brand’s actions and decisions.
- Brand Personality: Determine the human characteristics and traits that your brand embodies.
3. Creating a Unique Brand Positioning
- Value Proposition: Define what makes your brand unique and why customers should choose you over competitors.
- Competitive Analysis: Analyze your competitors to identify gaps and opportunities for differentiation.
4. Developing Brand Assets
- Logo and Visuals: Design a memorable logo and establish a consistent visual style, including color schemes, typography, and imagery.
- Brand Voice and Messaging: Develop a distinct voice and messaging that reflect your brand’s personality and values.
5. Building Brand Awareness
- Marketing and Advertising: Use various channels (social media, content marketing, SEO, PPC, etc.) to increase brand visibility.
- Public Relations: Engage with media and influencers to generate buzz and credibility.
6. Ensuring Brand Consistency
- Brand Guidelines: Create a comprehensive brand style guide to ensure consistency across all communications and touchpoints.
- Training and Communication: Educate employees and stakeholders about the brand to ensure alignment and consistency in representation.
7. Engaging with Your Audience
- Content Marketing: Produce valuable and relevant content that resonates with your audience.
- Social Media Engagement: Actively engage with your audience on social media platforms to build relationships and community.
- Customer Feedback: Listen to and act on customer feedback to improve and adapt your brand.
8. Building Brand Loyalty
- Customer Experience: Provide exceptional customer service and memorable experiences.
- Loyalty Programs: Implement loyalty programs to reward repeat customers and foster long-term relationships.
- Personalization: Offer personalized experiences and communications based on customer preferences and behaviors.
9. Measuring and Evolving
- Performance Metrics: Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as brand awareness, engagement, loyalty, and equity.
- Adaptation: Continuously refine and evolve your brand strategy based on market trends, customer feedback, and performance data.
10. Investing in Long-Term Growth
- Innovation: Stay ahead of the curve by innovating and adapting to changing market conditions and customer expectations.
- Sustainability: Integrate sustainable practices and social responsibility into your brand to enhance reputation and appeal to conscious consumers.
Brand building is an ongoing process that requires dedication, creativity, and a deep understanding of your market and audience. By focusing on these key elements, you can create a strong, enduring brand that resonates with customers and stands out in the marketplace.
Are Brands Born or Built ?
Brands are built, not born. While a brand might have inherent qualities or a unique story from its inception, it is through deliberate and consistent efforts that a brand is developed and established in the market. Here’s why and how brands are built:
1. Initial Creation
- Concept and Vision: Every brand starts with an idea, vision, or mission. This is the foundation, but it’s just the beginning.
- Naming and Identity: The creation of a name, logo, and initial visual identity sets the stage for the brand’s future development.
2. Strategic Development
- Brand Positioning: Identifying the unique value proposition and positioning the brand in the market relative to competitors.
- Target Audience: Defining and understanding the target audience to tailor the brand’s messaging and offerings.
3. Building Awareness and Recognition
- Marketing and Advertising: Using various channels to create awareness and recognition. This involves strategic campaigns, advertising, and promotions.
- Public Relations: Engaging with media and influencers to gain credibility and visibility.
4. Establishing Trust and Credibility
- Quality and Consistency: Delivering consistent quality in products and services builds trust over time.
- Customer Experience: Providing exceptional customer service and experiences fosters positive perceptions and loyalty.
5. Engagement and Relationship Building
- Content and Social Media: Creating valuable content and engaging with customers on social media platforms to build relationships.
- Community Building: Developing a community around the brand to foster loyalty and advocacy.
6. Evolving and Adapting
- Feedback and Improvement: Listening to customer feedback and continuously improving products, services, and brand messaging.
- Innovation: Adapting to market changes and innovating to stay relevant and ahead of competitors.
7. Long-Term Investment
- Sustained Efforts: Consistent and long-term investment in branding activities ensures the brand remains strong and grows over time.
- Brand Equity: Building brand equity through positive associations, customer loyalty, and perceived value.
Case Studies
- Coca-Cola: Started as a single product in 1886, Coca-Cola built its brand over decades through strategic marketing, consistent branding, and global expansion.
- Apple: Founded in 1976, Apple’s brand was built through innovative products, a focus on design and user experience, and iconic marketing campaigns.
Conclusion
While the seed of a brand may be “born” with its initial concept, name, and identity, it is through strategic and sustained efforts that a brand is truly built. Building a brand requires time, resources, and a clear understanding of the market and audience. Brands that successfully navigate this process can achieve lasting recognition, loyalty, and value.
Brand Building Vs Branding
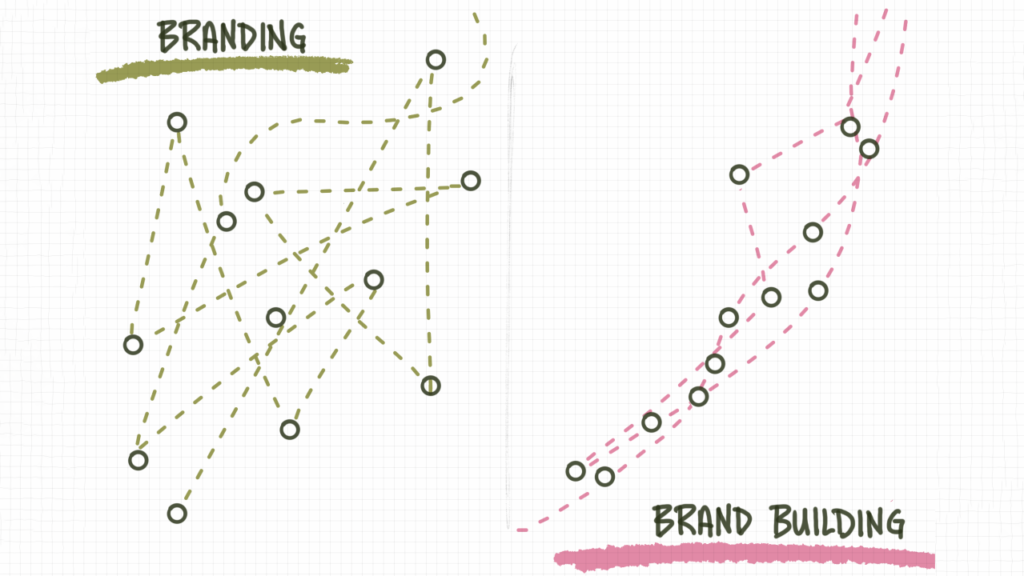
Brand building and branding are related but distinct concepts in the realm of marketing. Understanding the difference between the two can help in effectively managing and growing a brand.
Brand Building
Definition: Brand building is the comprehensive, long-term process of creating and strengthening a brand’s identity, presence, and reputation in the market. It encompasses all the strategic efforts and activities aimed at developing a brand that resonates with the target audience and stands out in the marketplace.
Key Components:
- Brand Identity Development: Creating the visual and verbal elements of the brand, including the logo, color scheme, typography, and brand voice.
- Brand Positioning: Defining the unique value proposition and positioning the brand to differentiate it from competitors.
- Brand Awareness: Implementing marketing and advertising strategies to increase visibility and recognition.
- Brand Loyalty: Building strong emotional connections with customers to foster loyalty and repeat business.
- Customer Engagement: Engaging with the audience through various channels to build relationships and community.
- Brand Consistency: Ensuring all brand communications and interactions are consistent across all touchpoints.
- Long-Term Growth: Continuously evolving and adapting the brand to changing market conditions and customer preferences.
Goal: The goal of brand building is to create a strong, lasting brand that enjoys high recognition, trust, and loyalty among its target audience.
Branding
Definition: Branding is the specific practice of actively shaping and managing a brand. It involves the use of various techniques and strategies to create a desired perception of the brand in the minds of consumers.
Key Components:
- Brand Design: Developing the visual elements of the brand, such as logos, packaging, and website design.
- Brand Messaging: Crafting and delivering the brand’s messaging through advertising, content marketing, and public relations.
- Brand Experience: Ensuring that every customer interaction with the brand aligns with the brand’s identity and values.
- Brand Guidelines: Establishing guidelines to maintain consistency in how the brand is represented across all channels and by all employees.
- Brand Communication: Engaging in ongoing communication with the target audience to reinforce the brand’s positioning and values.
Goal: The goal of branding is to shape and manage the brand’s perception, ensuring it aligns with the desired image and resonates with the target audience.
Key Differences
- Scope: Brand building is a broader, long-term process that includes all activities involved in creating and sustaining a brand. Branding, on the other hand, is a component of brand building, focused on the specific actions and strategies used to shape the brand’s perception.
- Duration: Brand building is an ongoing effort that evolves over time, while branding activities can be short-term campaigns or initiatives aimed at reinforcing the brand’s image.
- Activities: Brand building involves strategic planning, market research, and long-term growth efforts, while branding includes the creation of visual and verbal brand elements, marketing campaigns, and communication strategies.
Conclusion
Brand building is about creating a strong, enduring brand through a comprehensive, strategic approach, while branding is about managing and shaping the brand’s perception through specific activities and techniques. Both are essential for a successful brand, working together to establish and maintain a positive and lasting presence in the market.
Why Brand Perception is important ?

Brand perception is crucial for several reasons, as it directly influences a company’s success and long-term sustainability. Here’s why brand perception is so important:
1. Customer Trust and Loyalty
- Trust Building: Positive brand perception fosters trust among customers. When people perceive a brand as reliable and credible, they are more likely to trust its products or services.
- Loyalty: A strong, positive perception leads to customer loyalty, as consumers are more likely to return to a brand they perceive favorably.
2. Competitive Advantage
- Differentiation: In a crowded marketplace, a favorable brand perception helps distinguish a brand from its competitors.
- Preference: Customers are more likely to choose a brand they perceive positively over others, even if the price is higher.
3. Pricing Power
- Premium Pricing: Brands with strong, positive perceptions can command higher prices because customers associate them with higher value and quality.
- Reduced Price Sensitivity: Consumers are less likely to be swayed by lower prices from competitors if they perceive your brand as superior.
4. Customer Acquisition and Retention
- Attraction: Positive perception attracts new customers who are influenced by the brand’s reputation and image.
- Retention: Satisfied customers with a positive perception of the brand are more likely to remain loyal and make repeat purchases.
5. Word-of-Mouth and Advocacy
- Recommendations: Satisfied customers are more likely to recommend the brand to others, acting as brand advocates.
- Positive Reviews: Good brand perception leads to positive reviews and testimonials, which can influence potential customers.
6. Employee Morale and Recruitment
- Attracting Talent: A strong brand perception can attract top talent who want to be associated with a reputable and respected brand.
- Employee Pride: Employees are more likely to feel proud and motivated when working for a brand that is well-perceived, leading to higher job satisfaction and productivity.
7. Crisis Resilience
- Buffer in Crisis: Brands with strong, positive perceptions are better able to withstand negative events or crises. Loyal customers are more likely to forgive mistakes if they have a generally favorable view of the brand.
- Reputation Recovery: Positive perception aids in faster recovery from reputational damage, as the established goodwill can mitigate the impact of negative incidents.
8. Marketing and Communication Efficiency
- Reduced Costs: A positive brand perception can reduce the need for extensive marketing efforts, as word-of-mouth and organic reach become more effective.
- Message Reception: Marketing messages are more likely to be received positively if the brand already has a good reputation.
9. Market Expansion
- Easier Entry: Brands with strong, positive perceptions find it easier to enter new markets or launch new products, as the existing reputation paves the way for acceptance.
10. Investor Confidence
- Attracting Investment: Investors are more likely to invest in brands with positive market perceptions, seeing them as lower-risk and higher-potential.
- Valuation: Strong brand perception often translates to higher company valuations and better financial performance.
Conclusion
Brand perception shapes how customers, employees, investors, and the market view and interact with a brand. It influences trust, loyalty, competitive positioning, and overall success. Investing in building and maintaining a positive brand perception is essential for long-term growth and sustainability.
Brand Lifecycle

The brand lifecycle refers to the stages a brand goes through from its inception to its decline. Understanding the brand lifecycle helps companies strategize effectively at each stage to maximize growth, maintain relevance, and manage decline. Here are the typical stages of the brand lifecycle:
1. Introduction Stage
Characteristics:
- Brand Creation: Development of the brand’s identity, including name, logo, and positioning.
- Market Entry: Launching the brand into the market with initial products or services.
Strategies:
- Awareness Building: Focus on creating brand awareness through advertising, PR, and promotions.
- Educating the Market: Informing potential customers about the brand’s unique value proposition.
- Trial Incentives: Offering discounts, samples, or trials to encourage initial purchases.
2. Growth Stage
Characteristics:
- Increasing Sales: Rapid growth in sales as the brand gains acceptance and market share.
- Market Penetration: Expanding the customer base and deepening market penetration.
Strategies:
- Brand Differentiation: Emphasizing what makes the brand unique to stand out from competitors.
- Product Expansion: Introducing new products or variations to meet diverse customer needs.
- Strengthening Distribution: Expanding distribution channels to reach a broader audience.
3. Maturity Stage
Characteristics:
- Market Saturation: Sales growth slows down as the market becomes saturated.
- Intense Competition: Increased competition as other brands seek to capture market share.
Strategies:
- Brand Loyalty: Focusing on retaining existing customers through loyalty programs and exceptional customer service.
- Innovation: Introducing new features, improvements, or variations to keep the brand fresh and relevant.
- Efficiency: Optimizing operations and marketing efforts to maintain profitability.
4. Decline Stage
Characteristics:
- Decreasing Sales: Sales begin to decline as market conditions change or consumer preferences shift.
- Reduced Market Relevance: The brand may struggle to stay relevant in a changing market.
Strategies:
- Rebranding or Revitalization: Refreshing the brand’s image, updating the brand identity, or repositioning in the market.
- Product Phasing: Gradually phasing out less profitable products or lines.
- Cost Management: Reducing costs and optimizing resources to maintain profitability.
5. Renewal or Retirement Stage
Characteristics:
- Renewal: Successful revitalization efforts can rejuvenate the brand, leading to a new growth phase.
- Retirement: If renewal is not feasible, the brand may be retired or merged with another brand.
Strategies:
- Renewal:
- Innovation: Developing new products or services that align with current market trends.
- Marketing Refresh: Launching new marketing campaigns to re-engage the audience.
- Retirement:
- Gradual Phase-Out: Slowly discontinuing the brand while managing remaining inventory.
- Mergers or Acquisitions: Integrating the brand with another to leverage combined strengths.
Conclusion
The brand lifecycle provides a framework for understanding the different phases a brand experiences and the strategies needed to navigate each stage. By recognizing where a brand stands in its lifecycle, companies can implement appropriate strategies to maximize growth, maintain relevance, and manage decline effectively.
How Can LAK help build your Brand ?
We are a team of professionals with decades of experience in management consulting & change management and possess hands on experience in designing and implementing Strategies & Business Processes, People Management, Branding, Marketing & PR, Finance, Accounting & Taxation. We have associate partners in various industries who play a significant role in scaling up operations and have deep market insights. Connect with us and lets start building your brand together.
